Antigen Depot Effect
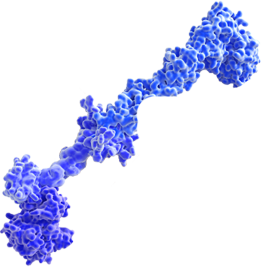
IP-001 is a macromolecule with a cationic backbone that generates a depot effect, enhancing antigen retention at the injection site and allowing for a prolonged interaction with the immune system.Recruitment of Innate Immune Cells
IP-001 increases innate immune cell infiltration into the injection site and activates multiple myeloid cell populations, especially antigen-presenting cells (APCs) like dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages.Activated by IP-001
Innate Immune System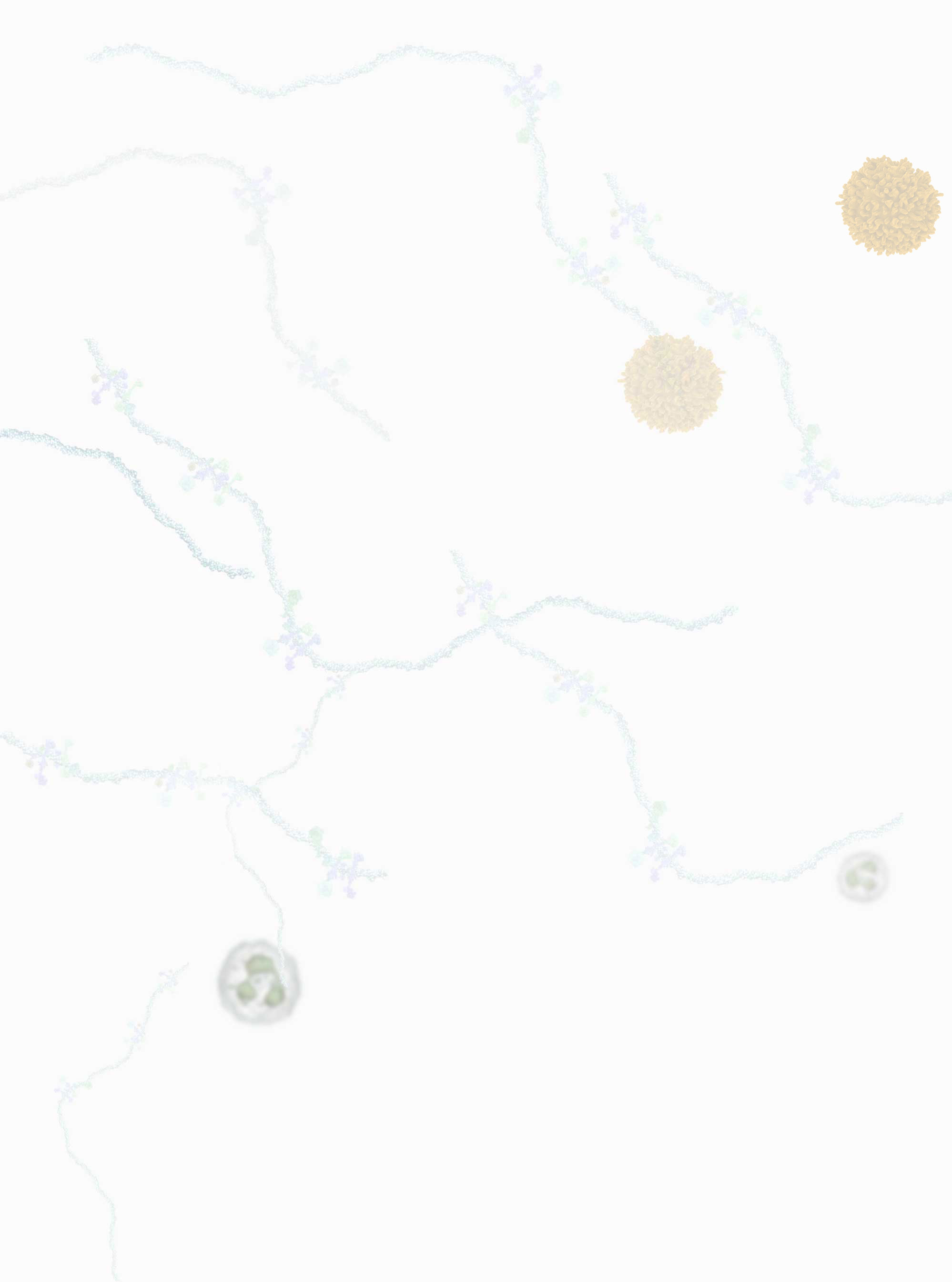
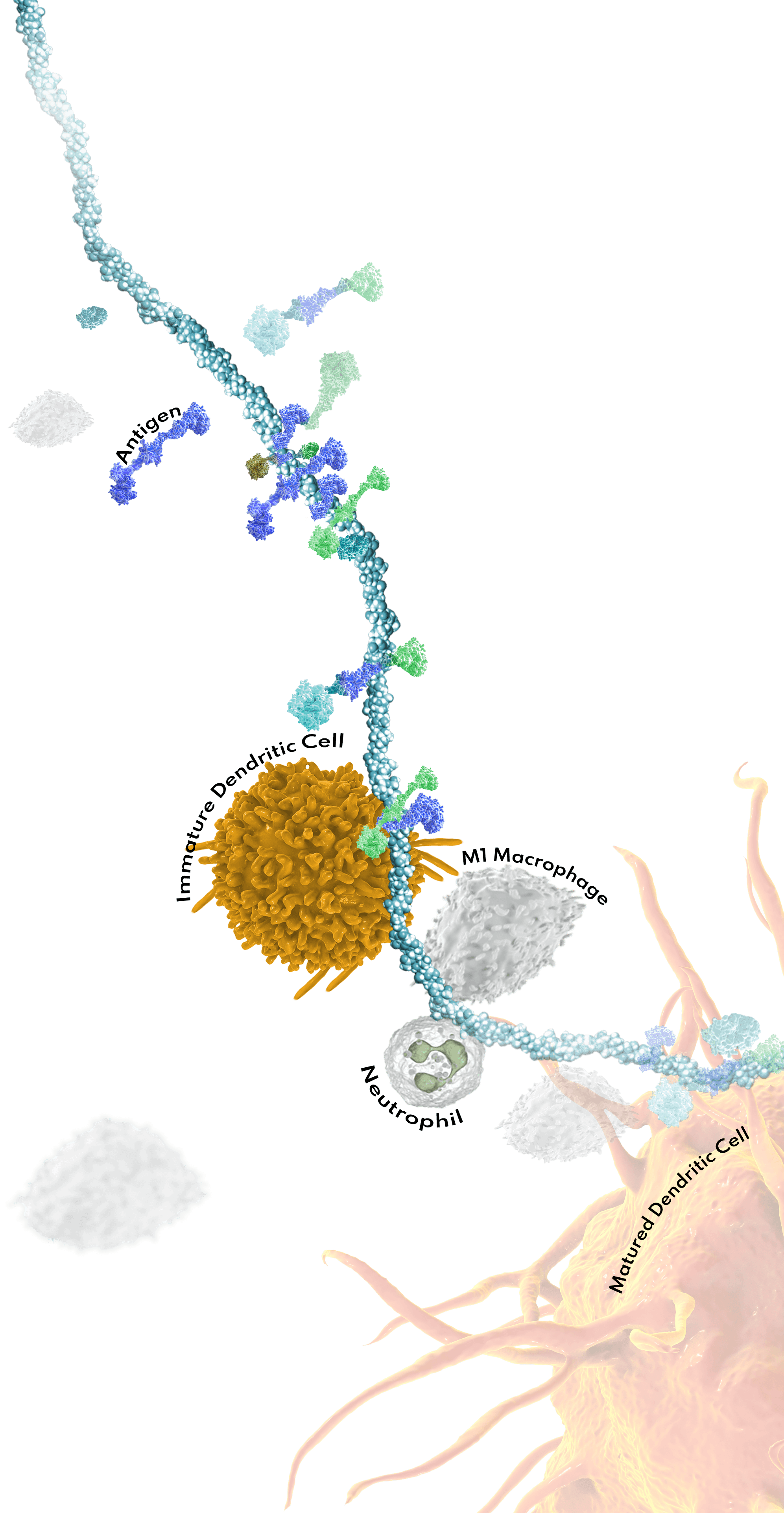
Immunological Activation and Enhanced Antigen Uptake
IP-001 increases the uptake of antigens and activates APCs through the upregulation of major histocompatibility complex II (MHC-11) and co-stimulatory molecules such as C40 and B7-family CD80 and CD86. This is achieved in part through the production of type-1 interferon via the cGAS-STING pathway and IL-1b from the inflammasome pathway.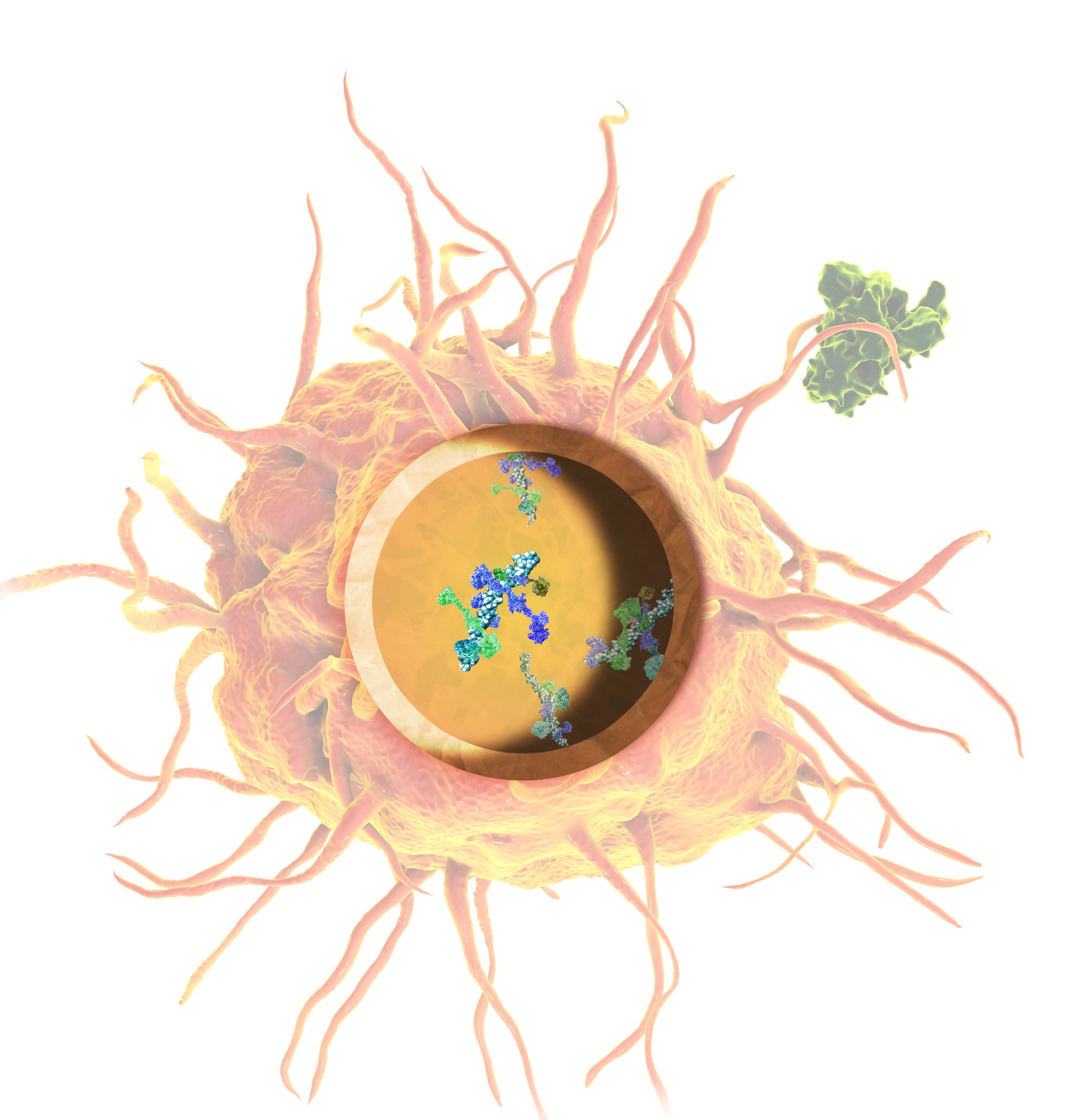
Activation by IP-001
The ignited systemic, adaptive immune response seeks out and eliminates its target throughout the body.
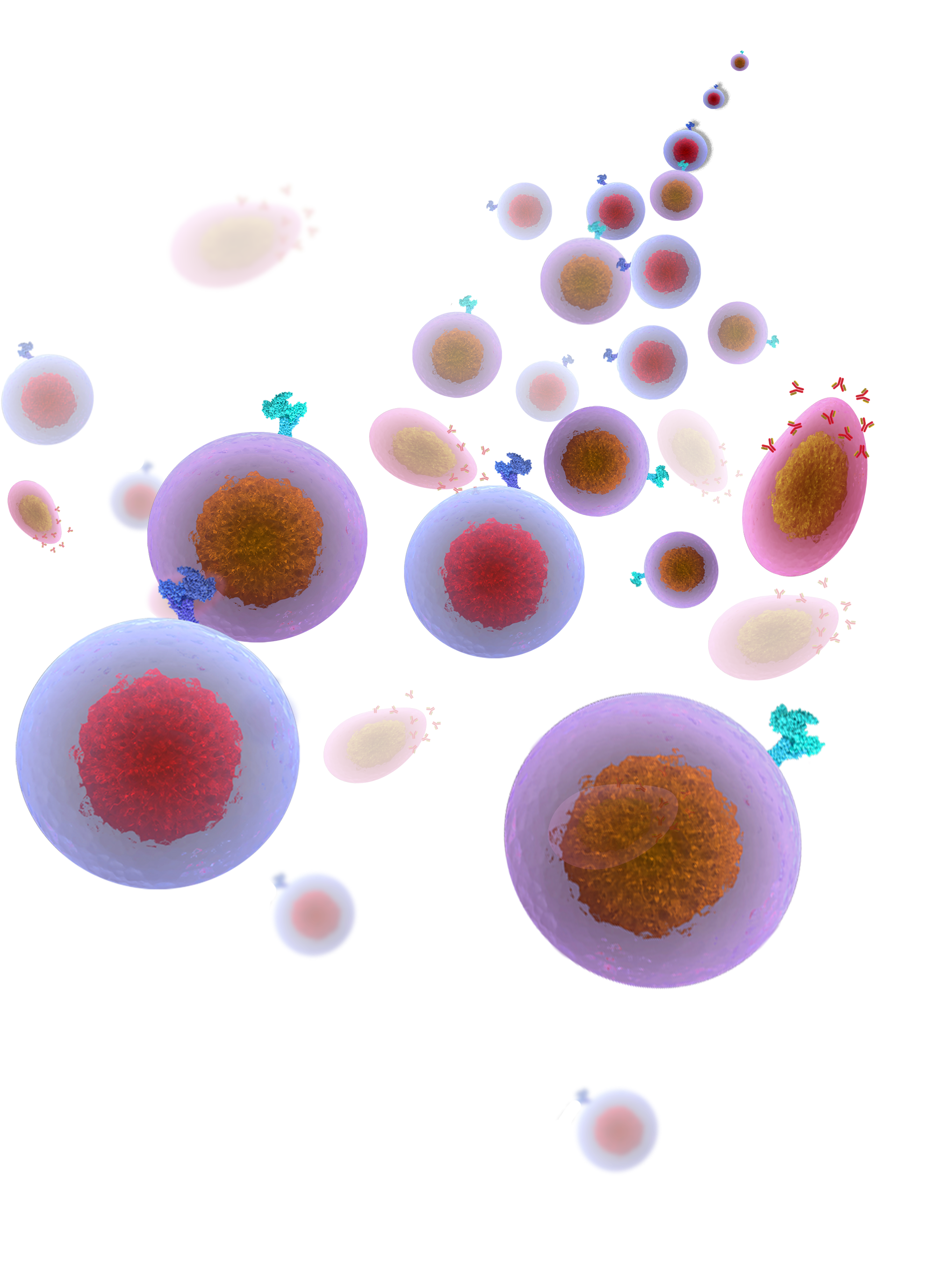


CD8+ T Cell
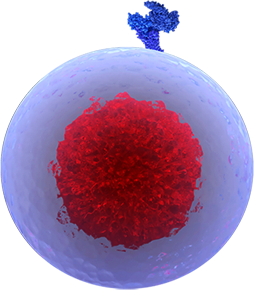
Like all T cells, these are white blood cells that originate from the bone marrow and develop in the thymus. CD8+ T cells, also known as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), are the primary effectors of cell-mediated adaptive immune responses once activated by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). CTLs are armed with cell-death-inducing surface ligands and effector molecules to kill aberrant cells. They are one of the most potent immune effector cells and are capable of killing cancer cells and virally infected cells.
CD4+ T Cell
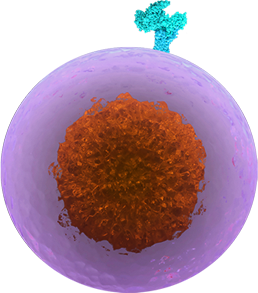
This subtype of T cells expresses the signaling protein CD4 and recognizes peptides presented to them on APCs. They are classified as “helper” T cells because, rather than acting as a killer of damaged cells, they trigger the body's immune response to aberrant cells through other cells (like CD8+ cells). Depending on the environmental signal they receive, CD4 T cells can differentiate into various helper phenotypes that can direct the specific types of adaptive immune responses following antigen presentation.
B Cell
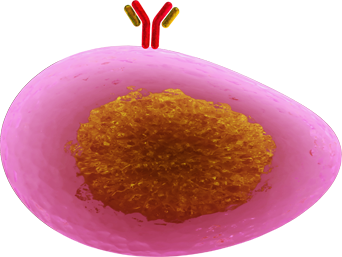
B cells are a type of white blood cell that originates in the bone marrow. They can act as APCs but can also differentiate into clones of plasma cells that secrete a specific antibody upon encountering a particular foreign antigen. Some B cells turn into long-lasting memory cells that can produce antibodies in a much larger quantity within a shorter timeframe on subsequent encounters of the same antigen. This mechanism is an important basis of vaccination against multiple infectious diseases.
Antigen Depot Effect
IP-001 is a macromolecule with a cationic backbone that generates a depot effect, enhancing antigen retention at the injection site and allowing for a prolonged interaction with the immune system.Recruitment of Innate Immune Cells
IP-001 increases innate immune cell infiltration into the injection site and activates multiple myeloid cell populations, especially antigen-presenting cells (APCs) like dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages.Activated by IP-001
Innate Immune System




Immunological Activation and Enhanced Antigen Uptake
IP-001 increases the uptake of antigens and activates APCs through the upregulation of major histocompatibility complex II (MHC-11) and co-stimulatory molecules such as C40 and B7-family CD80 and CD86. This is achieved in part through the production of type-1 interferon via the cGAS-STING pathway and IL-1b from the inflammasome pathway.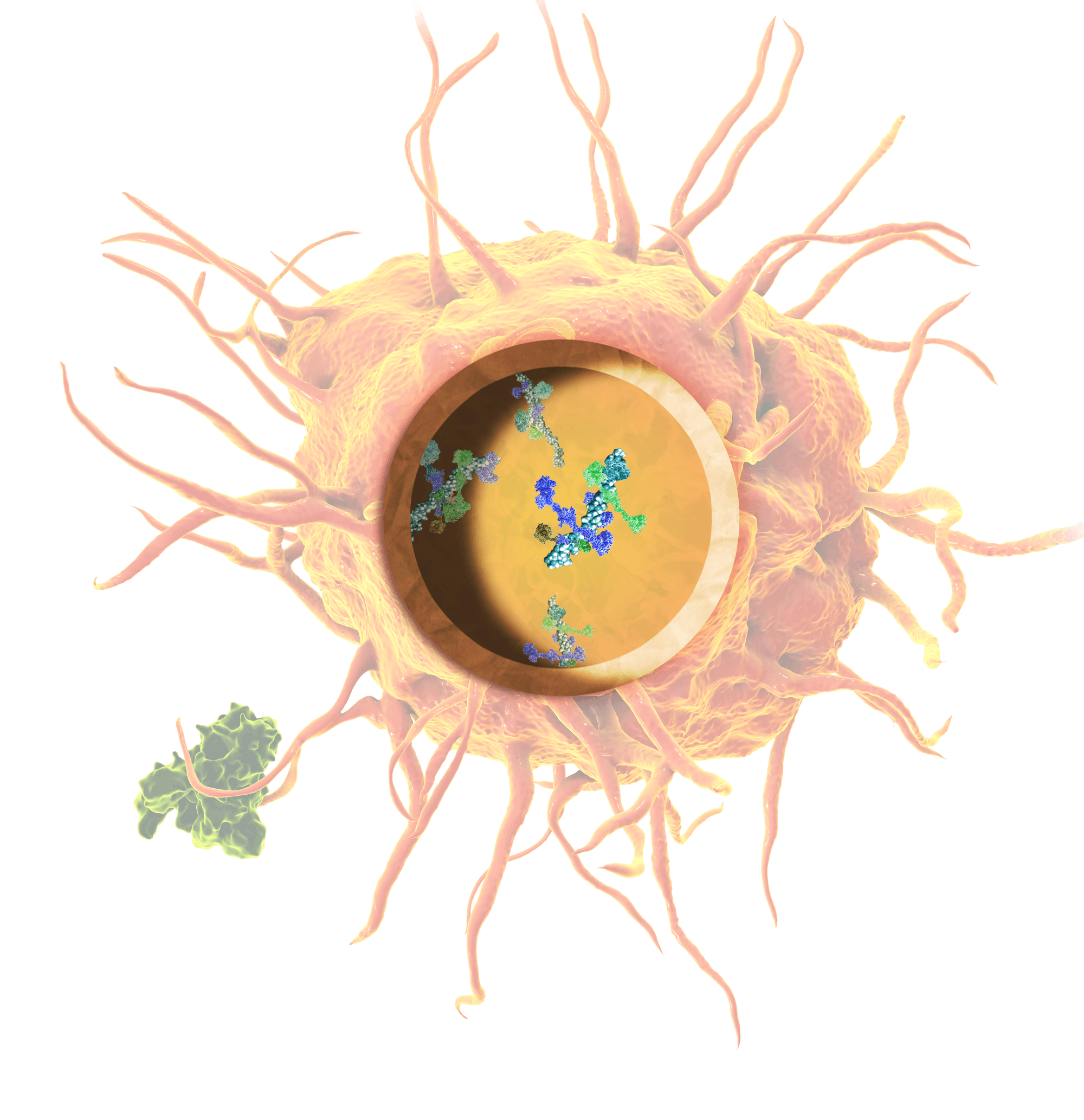
Activation by IP-001
The ignited systemic, adaptive immune response seeks out and eliminates its target throughout the body.




CD8+ T Cell

Like all T cells, these are white blood cells that originate from the bone marrow and develop in the thymus. CD8+ T cells, also known as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), are the primary effectors of cell-mediated adaptive immune responses once activated by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). CTLs are armed with cell-death-inducing surface ligands and effector molecules to kill aberrant cells. They are one of the most potent immune effector cells and are capable of killing cancer cells and virally infected cells.
CD4+ T Cell

This subtype of T cells expresses the signaling protein CD4 and recognizes peptides presented to them on APCs. They are classified as “helper” T cells because, rather than acting as a killer of damaged cells, they trigger the body's immune response to aberrant cells through other cells (like CD8+ cells). Depending on the environmental signal they receive, CD4 T cells can differentiate into various helper phenotypes that can direct the specific types of adaptive immune responses following antigen presentation.
B Cell

B cells are a type of white blood cell that originates in the bone marrow. They can act as APCs but can also differentiate into clones of plasma cells that secrete a specific antibody upon encountering a particular foreign antigen. Some B cells turn into long-lasting memory cells that can produce antibodies in a much larger quantity within a shorter timeframe on subsequent encounters of the same antigen. This mechanism is an important basis of vaccination against multiple infectious diseases.



